At Huggy, we
Huggy Partner, let's promote the Culture of Privacy together
The more we talk about data privacy, the more we develop technologically and economically.
Personal Data and
Processing of Personal
Data
What is personal data?
Any information that can lead to the identification of a natural person, directly or indirectly.
Some examples are:
• Registration Data;
• Location Data;
• Email Addresses;
• Cookies;
• Consumption History.
What is the processing of personal data?
Any activity that uses some form of personal data.
Some examples are:
• collecting customer personal data, such as CPF or address;
• storing said data in forms, systems, or emails;
• sharing personal data with other companies, government, or partner;
• analyzing data, such as purchase history, to propose exclusive promotions.
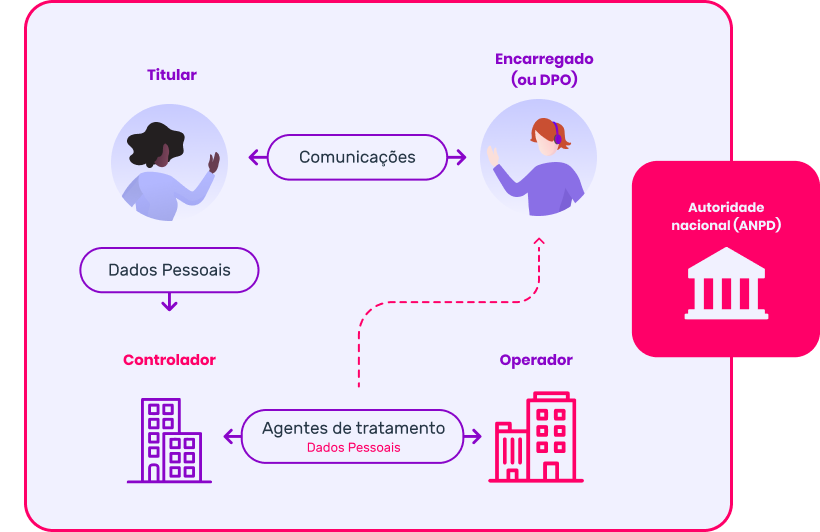
What are personal data processing agents?
The processing of personal data can be carried out by two processing agents: the controller and the operator.
• The controller is the one responsible for decisions regarding the processing of personal data.
They decide which data will be collected, stored, and shared, how, and for what purposes;
• The operator is the one who processes personal data on behalf of the controller,
following the guidelines set by the latter.
Both are responsible for meeting the rights of the data subject and protecting their personal data.
And the Data Protection Officer ('DPO')?
The Data Protection Officer, known as “DPO”, has the important mission of acting as a communication channel between the organization that processes personal data, the data subjects, and the National Data Protection Authority (ANPD).
They will be a key agent in creating a culture of privacy within the organization, guiding employees and contractors of the entity regarding practices to be taken concerning the protection of personal data.
Pretty easy to understand,
right?
Now let's get to the laws!
General Data Protection Law - LGPD
The General Data Protection Law - LGPD is the Brazilian law on personal data processing. With some exceptions, it applies to any person, natural or legal, that performs personal data processing activities*, such as Huggy partners who store customer data to provide better and more personalized service.
General Data Protection Regulation - GDPR
The General Data Protection Regulation - GDPR is the European law on personal data processing. Although it is not in force in Brazil, it requires Brazilian companies that process personal data of customers or users residing in European Union countries to comply with it.
What is the scope of application of the LGPD and GDPR?
Any personal data processing activity must be carried out in accordance with the applicable law. This includes the processing of:
• consumers;
• employees;
• app users;
• representatives of partner companies.
Which areas of companies are most impacted by LGPD and GDPR?
Essentially, all sectors of organizations are affected by the new personal data processing paradigm in some way, but we can mention the areas of Marketing, Sales, IT, Products, and HR as the main ones.
How can I know if a personal data processing is possible or legal?
All personal data processing must be carried out based on one of the legal grounds corresponding to a legitimate purpose. Examples of these are:
• consent of the data subject;
• legitimate interest of the processing agent or third parties;
• execution of a contract;
• compliance with a legal or regulatory obligation;
• exercise of the right of defense in judicial or administrative proceedings;
• among others.
According to the legislation, the consent of a person is not always necessary for personal data processing, and it should even be avoided in some cases. Therefore, a legal analysis of each personal data processing carried out by an organization is essential to ensure that there is a legal basis that legitimizes it.
The idea, therefore, is not to make processing impossible, but to ensure it is done safely, using the minimum amount of personal data necessary to achieve a specific and legitimate purpose, providing maximum transparency to the data subject regarding how the data is processed.
So, what changes?
The LGPD empowers personal data subjects, providing them with rights to be exercised throughout the existence of the personal data processing by the institution holding the information.
privacyPortal.goodFacylit.acordions.6.descriptionItem
What are the rights of personal data subjects?
There are many rights provided by the LGPD and GDPR. Among them, we highlight these five:
1 - the right to information for data subjects, including access to information about their personal data stored by third parties;
2 - correction of incorrect, outdated, or incomplete information;
3 - cancellation of authorization for data processing;
4 - data portability;
5 - deletion of data, in some cases.
Data subjects can request the exercise of these rights at any time from those responsible for the processing, who must maintain a dedicated channel for receiving requests and publicize it in their privacy policies.
What are the principles brought by the LGPD?
There are many principles brought by the LGPD and GDPR. Among them, we highlight these four:
1 - Purpose – It is no longer possible to process personal data for generic or indeterminate purposes. The processing of each piece of personal information must be carried out for specific, legitimate, explicit, and informed purposes to the data subject;
2 - Necessity (or minimization) – Companies can only use data that is indeed necessary to achieve their purposes;
3 - Free access – The data subject has the right to consult, simply and free of charge, all the data that the company holds about them;
4 - Transparency – All information about personal data processing carried out by the company must be available to the data subject in a clear, precise, and truthful manner.
What should be done to comply with LGPD and GDPR?
Some of the main measures of a compliance plan are:
• Map the entry and exit points of personal data in the organization;
• Appoint a Data Protection Officer (“DPO”) to lead the actions necessary to comply with data protection laws and manage data subject requests and communication with external authorities;
• Check if all personal data processing activities carried out by the organization are based on a legal ground and comply with the principles of the law;
• Identify risks and attention points in the processing activities and develop action plans with the implementation of privacy and information security policies, process reengineering, and team training;
• Clearly state on your pages the objectives for which each piece of personal data is being captured, and what processing is carried out;
• Create a dedicated channel for handling data subject requests;
• Provide, correct, or delete stored data of an individual if they request it with legal support;
• Amend terms of use, contracts, and privacy policies to transparently reflect the circumstances of personal data processing in the organization.
Compliance with LGPD and GDPR is an ongoing process that involves, including, a cultural and behavioral change within organizations - involving, for example, the alteration of various internal processes.
Therefore, the engagement of leadership and all sectors of the company is crucial to ensure that the actions instituted are adhered to in the work routines, through an effective awareness process.
Many other measures are necessary and advisable, so it is important to have a technical team and lawyers specializing in personal data protection and the digital universe.